Introduction:
In pursuit of our objective to build technologies for communities to enhance natural resource management (NRM), the CoRE Stack (Commoning for Resilience and Equality) is addressing shortcomings in NRM supply- and demand- planning by introducing a systematic data-driven approach to understand the socio-ecological sustainability of landscapes, and participatory, community-friendly digital tools for communities to propose action plans.
Being built through a rich and growing collaboration network between IIT Delhi, IIT Palakkad, Gram Vaani, WELL Labs, Magasool, GIZ, FES, Common Ground, and Rainmatter Foundation, the CoRE Stack initiates the empowerment process in communities by leveraging data to facilitate a deeper understanding of their landscape. Through data-driven insights, communities gain knowledge about crucial factors such as water availability, forest health, topography, and land use. This foundational information forms the basis for informed decision-making. Being designed as a Digital Public Good, the CoRE stack enables an open-access co-creation network to innovate and scale digital technology solutions for ecosystem sustainability.
Progress Update: We are delighted to share significant advancements in various dimensions of the stack. The stack comprises four key layers. At the first layer, we leverage machine learning on satellite imagery to generate innovative geo-spatial layers, depicting changes in cropping intensity, water-table levels, health of water bodies, forests and plantations, and welfare fund allocation over the years. The second layer involves the generation of rich analytics on diverse socio-ecological variables, including aspects of fairness and equity in resource distribution, particularly focusing on groundwater and surface water. You can check out many of these layers and simple analytics on a Google Earth Engine application. These datasets and analytics feed into the third layer, where they will serve as inputs for APIs used by tools. This will enable communities, social enterprises, and other stakeholders to gain insights into any landscape, report new findings, and plan for sustainable natural resource management, including groundwater and forests. The fourth layer involves developing tools empowering communities to advocate for NRM assets promoting resilience and sustainability under relevant government and CSR programs. It also includes monitoring the impact of interventions over time.
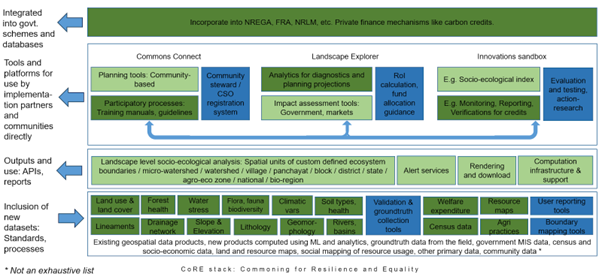
Fig 1: CoRE Stack Layers
We recently field tested some aspects with promising results. Interactions and demonstrations during the field testing have been invaluable and are helping us to fine-tune our solution to address relevant needs.
Currently, our tool stands as a robust resource for facilitators, providing them with a profound understanding of the landscape and socio-ecological dynamics. Offering detailed insights into groundwater and surface water bodies, as well as agricultural practices, the tool empowers facilitators to effectively illustrate and communicate these complex dynamics to the community. This heightened awareness fosters greater community engagement and participation.
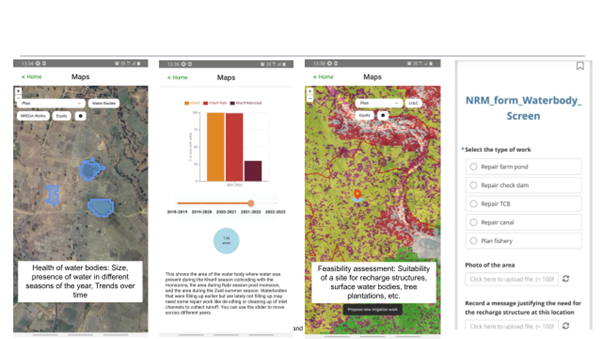
Fig 2: Detailed insights on the health of surface water bodies – from data to action
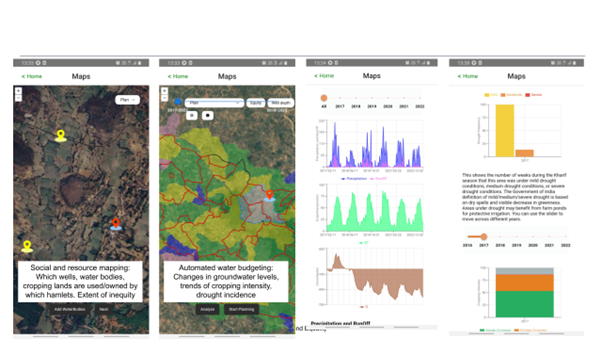
Fig 3: Detailed insights on the state of groundwater levels
Plan for the Next Quarter: The plan for the upcoming quarter is to improve and initiate pilot tests of various components of the stack, including a robust data validation exercise for several machine learning based novel datasets that we are computing.
- Tool Refinement: Fine-tune the existing tool based on valuable feedback received during field testing.
- Enhancements and New Features: Incorporate new features and functionalities to enrich the user experience, such as the integration of plantations and forests data, tutorials and awareness modules for community members, and other tools for landscape interaction.
- Dataset Hosting: Build a robust dataset hosting infrastructure for various layers to ensure seamless accessibility.
- Self-Learning Module: Develop a self-learning module titled “Know Your Landscape” to empower users with in-depth knowledge and insights into their surroundings.
Call to Action: As we continue on this journey of innovation, we invite organizations that share our vision to engage in discussions with us on new use-cases as these perspectives are crucial in shaping the impact of our initiative. We extend a warm invitation to explore collaborative opportunities and discover how our collective efforts can drive meaningful change.
We express our gratitude for the continued support that has fueled our progress. As we move forward, we remain committed to advancing our project and creating positive impact.





